


With the advancement of power electronics technology and the increasing integration of microgrids into the power grid, flexible DC distribution networks are becoming a research focus worldwide due to their advantages, such as lower line construction costs, reduced power loss, higher power supply reliability, and lower microgrid integration costs.
To conduct in-depth research on flexible DC distribution technology, Shenzhen Power Supply Bureau Co., Ltd. took the lead, collaborating with institutions like Tsinghua University and Zhejiang University to undertake the research for the Ministry of Science and Technology's 863 Program project—"Research and Application of Key Technologies for Smart Distribution Based on Flexible DC." This project addresses prominent issues in urban AC distribution networks, such as power quality problems and the rapid development of distributed generation. It investigates the use of flexible DC technology in urban distribution networks, including dedicated power supply to specific users and using voltage source converters (VSC) to improve AC distribution power quality. Additionally, it explores technical solutions like directly connecting distributed generation and energy storage devices on the DC side to supply DC loads directly. These approaches aim to solve several critical problems in urban distribution networks and expand the application areas of flexible DC technology.
KeLiang utilized the RT-LAB real-time simulator to establish a hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) research and testing platform for a flexible DC distribution control and protection system. This platform played a crucial role in the project, assisting Shenzhen Power Supply Bureau in successfully completing the first-phase simulation experiments for the flexible DC distribution network.
Currently, domestic research on DC distribution networks—covering steady-state analysis, fault analysis, operational control, and power quality—primarily involves analysis and verification using digital simulation software. However, pure digital simulation software cannot accurately replicate the response characteristics of protection devices when studying flexible DC distribution protection systems. It fails to anticipate potential issues in hardware implementation and is not conducive to testing controller communication and coordination between different control layers or devices.
Furthermore, building a user-friendly digital model for real-time simulation of flexible DC distribution networks poses significant technical challenges, particularly in accurately simulating MMC voltage source converters (VSC) and high-frequency DC transformers with switching frequencies reaching tens of kilohertz.
First, a sufficiently small simulation time step is required to fully capture fast electromagnetic transient phenomena. Second, the sampling time step for high-frequency switching signals must be below 1 microsecond to accurately simulate controller performance. Additionally, the simulator must be scalable, capable of integrating high-frequency power electronic devices with other equipment or the grid for comprehensive system performance testing. Finally, application developers need to master its use and perform secondary development with low cost and high efficiency.
To address these challenges, OPAL-RT developed eFPGAsim, an FPGA-based real-time model software suite. eFPGAsim employs advanced eHS technology to simulate circuits with sub-microsecond time steps. Users can model using graphical tools. eHS analyzes the circuit grid and automatically constructs the matrix-based circuit on the FPGA without requiring FPGA programming. Moreover, eHS models can be seamlessly integrated with the RT-LAB simulator to achieve multi-rate, multi-domain simulation—for example, simulating power electronics subsystems with time steps below 1 microsecond while simulating the connected grid with steps of 20 to 50 microseconds.
Based on the RT-LAB flexible DC distribution real-time simulation platform, KeLiang completed the modeling of a flexible DC distribution network system that includes key conversion equipment, distributed generation, energy storage systems, and AC/DC loads. Using this platform, hardware-in-the-loop fault testing was conducted on the protection devices of the flexible DC distribution network for the AC side, inside the converters, and on the DC lines. This validated the effectiveness of the key equipment modeling for the DC distribution system and the control and protection strategies for the DC distribution system.
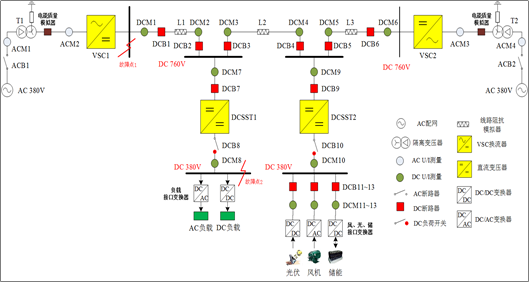
图1柔性直流配电系统实时仿真模型
Throughout this project, KeLiang provided comprehensive technical support and engineering implementation services, assisting the client in researching key technologies for DC distribution system control and protection and developing critical equipment. By seamlessly linking the RT-LAB real-time simulation system with protection devices, a hardware-in-loop testing platform based on a typical four-terminal flexible DC distribution network was established. Research was conducted on the typical architecture of flexible DC distribution systems, the functional architecture of control and protection, core equipment such as DC transformers, and energy management schemes. This yielded substantial research results and received unanimous recognition from the acceptance expert panel of the Ministry of Science and Technology.
The successful acceptance of this project significantly enhanced China's research level in the field of flexible DC distribution technology, promoted the development of domestic DC control and protection technology and power electronics equipment for distribution networks. It also provided a valuable reference for the subsequent second-phase 863 sub-project involving real-time simulation of a seven-terminal DC distribution system.